OOPs in Java: If we talk about java, the most important concept we need to know is OOPs. OOPs helps you to write clean, Organized and scalable code. Why oops is better than procedural is given
| Feature | OOP (Java) | Procedural |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Based on objects | Based on functions |
| Data Handling | Encapsulation | Global data |
| Reusability | High | Low |
| Security | Better | Weak |
| Example | Java, C++ | C, Pascal |
What is OOPs in Java
OOPs stands for Object Oriented Programming. It is a Java programming paradigm that focuses on creating objects that contain both data and behavior. Before starting the pillar of OOP, first we have to know about classes and objects.
Class
A class is a blueprint or, say, template of an object. It represent the set of properties or methods. Class is a logical entity. It is declared with the keyword class. And it does not take memory, but the object takes it when created.
Object
An object is the instance of a class. It is created from the class and actually holds the values of the properties and can use the methods. An object is a real entity, not logical like a class. It takes memory when it is created. In short, we say class is the template, and the object is the thing made from that template. While creating a home, first its map is passed; then, on the basis of that map, the home is made. Just like that, the home map is a class, and the home is a real entity like an object. It is created using a new keyword.
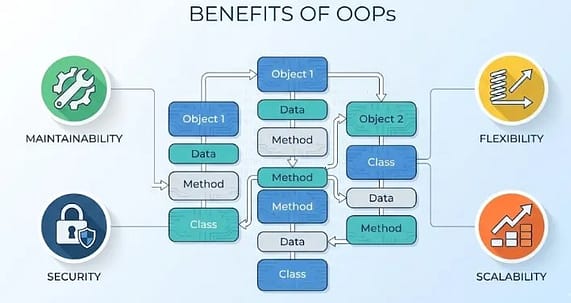
Benefits of Object-Oriented Programming:-
There are many Benefits of OOPs like:-
- Modularity
- Code reusability
- Improved security
- Flexible
- Scalable
- Maintainable
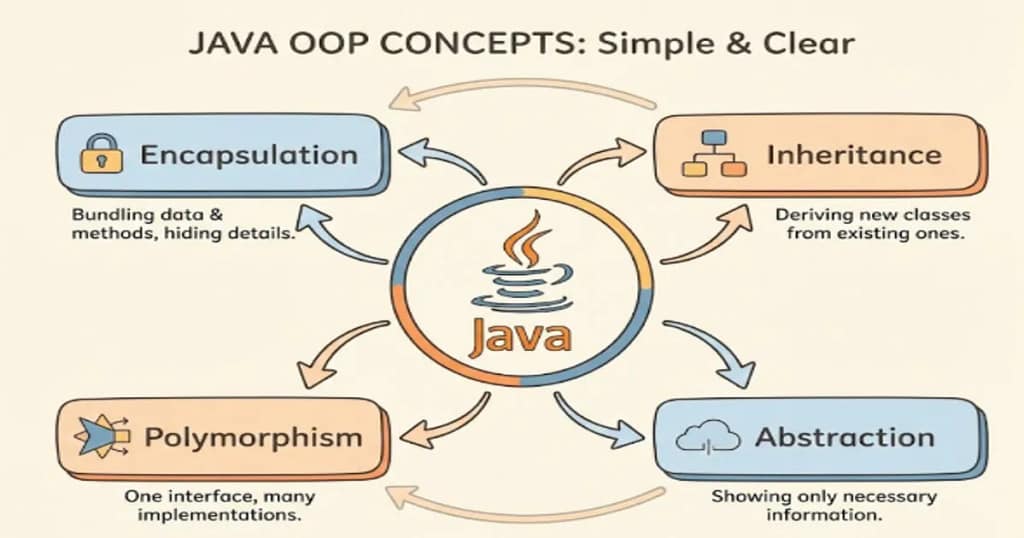
Pillar of Object Oriented Programming:-
The main four pillars of object-oriented programming are as follows:
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
1-Encapsulation
Binding of the data and methods together inside the single unit i.e class is called the encapsulation. It helps in hiding the internal data and access it by using getter and setter method. It is also known as data hiding. It is used for security reason.
Access Modifier
The Four Access modifier are as follows:-
| Access Modifier | Within Class | Within Package | Outside Package (Subclass) | Outside Package (Non-Subclass) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | Accessible from everywhere. |
| protected | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | It can be accessed everywhere except outside the package. |
| default (no keyword) | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | It can be access only within the same package. |
| private | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | It can be access in the same class. |
Advantage and Disadvantage Of Encapsulation
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Encapsulation protects data from unauthorized access | It Can increase code complexity |
| Improves code maintainability | More code needed (getters/setters) |
| Makes the class easy to change internally | Slower performance due to method calls |
| Enhances data security | Too much encapsulation can reduce flexibility |
2-Abstraction
To Hide the internal implementation and show only the necessary things is called Abstraction. For example: Switching on the fan no matter to know the mechanism of fan and its working. It is one of the most important pillar of the oops.
In Java we can achieve abstraction with abstract classes and interfaces.
| Feature | Abstract Class | Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword | abstract | interface |
| Methods | It Can have abstract + non-abstract methods | All methods are abstract by default |
| Variables | It Can have normal variables | Variables are public, static, and final |
| Multiple Inheritance | Not supported (cannot extend multiple classes) | A class can implement multiple interfaces. |
| Constructor | It Can have constructors | It Cannot have constructors |
| Access Modifiers | Methods can have any access modifier | Methods are public by default |
| Usage | When you want partial abstraction | When you want full abstraction |
| Speed | Slightly faster | Slightly slower |
| Inheritance | Class extends abstract class | Class implements interface |
Advantage and Disadvantage Of Abstraction
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Hides unnecessary details | Can be difficult to design correctly |
| Reduces complexity | Increases overall development time |
| Improves code readability | Requires good understanding of OOP |
| Makes code easier to maintain | Too much abstraction can confuse beginners |
Inheritance
Inheritance means to pass the properties and methods of the parent class to its child class. For example, in real life, children have the properties of their parents, like some of your properties match your father’s.
This is the parent class
class Vehicle {
String color = “Black”;
int wheels = 4;
void start() {
System.out.println(“Vehicle is starting…”);
}
}
This is the Child Class which inherit the Vehicle class using extend keyword
class Car extends Vehicle {
String model = “Sedan”;
void showDetails() {
System.out.println(“Color: ” + color);
System.out.println(“Wheels: ” + wheels);
System.out.println(“Model: ” + model);
}
}
Types of Inheritance
The types of inheritance and differences are given below: –
| Type of Inheritance | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Single Inheritance | In single Inheritance One class extend another class | Car extends Vehicle |
| Multilevel Inheritance | In Multilevel Inheritance a chain of inheritance like grandfather to father to Child clas s. | Sedan extends Car, Car extends Vehicle |
| Hierarchical Inheritance | In hierarchical inheritance, multiple classes inherit one parent class. | FinanceBlog & JavaBlog extend Blog |
| Multiple Inheritance | In Multiple Inheritance one class implements multiple interfaces. Java does not support this. | class SmartDevice implements Camera, MusicPlayer |
| Hybrid Inheritance | Mixing of one or more Types of Inheritance is called Hybrid Inheritance. | Sedan extends Car and implements GPS interface |
Advantage and Disadvantage Of Inheritance
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Promotes code reusability | Increases class dependency |
| Improves code structure | Changes in parent class can affect child classes |
| Reduces redundancy | Can lead to tight coupling |
| Supports polymorphism | Not suitable for all scenarios (e.g., multiple inheritance in Java not allowed) |
PolyMorphism
Polymorphism is made up of two greek words Poly=many, morph=forms. That allows objects to behave differently based on their specific class type. This means can take multiple forms.
Types of PolyMorphism
- Compile-Time Polymorphism
- Runtime Polymorphism
| Feature | Compile-Time Polymorphism | Runtime Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Also Known As | Static Binding / Early Binding | Dynamic Binding / Late Binding |
| How It Is Achieved | Method Overloading | Method Overriding |
| Decision Time | Resolved at compile time | Resolved at runtime |
| Performance | Faster (less overhead) | Slightly slower due to runtime decision |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible (supports dynamic behavior) |
| Inheritance Required | Not required | Required (works with inheritance) |
| Arguments / Parameters | Must differ (type, number, order) | Must be same as parent class method |
| Return Type | Can be different (in overloading) | Must match or be covariant |
| Example | Multiple methods with same name but different parameters | Child class overriding the parent class method |
Advantage and Disadvantage Of Polymorphism
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increases code reusability | Can make debugging more difficult |
| Makes code flexible and easier to extend | Overuse may lead to complex class structures |
| Improves maintainability | Runtime polymorphism can be slower |
| Reduces code duplication | Requires strong understanding of OOP concepts |
Common Interview Questions
- What is OOP in Java?
- Tell me how abstraction and encapsulation different?
- What is method overloading?
- What is method overriding?
- What is inheritance?
- Can Java support multiple inheritance?
- What is polymorphism?
- Java is a pure OOPs ? Why?
For official documentation, see Oracle Java Tutorials
Tech Skills That Can Increase Your Salary in 2026
How to Get Your First Tech Job
Best Tech Skills That Generate Passive Income in 2026
New Rule for IT Jobs in 2026 May Affect Fresher Hiring in India
Discover more from GroWithMoney
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

Pingback: What is Java? Why Java is Popular in 2025
Pingback: Tech Skills That Can Increase Your Salary in 2025
Pingback: How to Get Your First Tech Job: 9 Steps to Succeed
Pingback: 10 Top IT Companies Hiring Freshers– Eligibility, Salary
Pingback: TCS NQT 2026 Experience & Interview Tips – Digital Role
Pingback: Late Nights, College Stress, and Accidentally Finding AI Tools